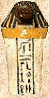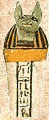Egyptian Symbolism
Egyptian Symbols were often used to depict ideas which would be difficult to elucidate through more concrete modes of expression. These ideas, thoughts, beliefs or perceptions often transcended the realms of reality. Egypt’s symbolic orientation can be confirmed by the fact that these symbols were not just used as architectural embellishments but they also held a sacrosanct place in rituals related to religion and magic.
Eye of Horus or Eye of Ra
Symbolizes healing and protection.
Egyptian Alphabet
Amenta
Ankh
The Ankh was used to symbolize eternal life or the existence of life in the netherworld. It is also used in Egyptian hieroglyphics to represent life and living.
However a completely contradictory theory states that the ankh is a symbol of the male and female genitalia. The ankh symbols found in the New Kingdom depicted a triangular structure in the loop at the upper end. This was interpreted as a representation of the triangular female mound. The long stump that extended down was considered to be the phallic representation while the horizontal dissecting line stood for the children or the union between the male and female
A third theory states the ankh symbolizes the movement of the sun or more specifically the sunrise with the central lop representing the sun or Ra a principle deity in the ancient Egyptian Religion while the stump was used to depicted the path of the sun and the horizontal line was used to represent the horizon.
Ba
Canopic Jars
During mummification the internal organs were removed and placed in four containers. These containers often have human or animal-headed stoppers.
Imsety: The human headed guardian of the liver
Hapy: The baboon headed guardian of the lungs
Duamutef: The jackal or wild dog headed guardian of the stomach.
Deshret
The Red Crown. This was the crown that represented Lower Egypt (northern).
Djed
Feather of Maat
Fetish of Osiris
Flail and Crook
- A symbol of royalty, majesty and dominion.
Hedjet
Ieb
 This symbol represents a heart. The Egyptian believed the heart was the center of all consciousness, even the center of life itself.
This symbol represents a heart. The Egyptian believed the heart was the center of all consciousness, even the center of life itself.Imenet
 These symbols represent the west or western desert AKA the land of the dead. The horizon on which Ra dies at night and enters the underworld.
These symbols represent the west or western desert AKA the land of the dead. The horizon on which Ra dies at night and enters the underworld.Ka
 The ka is usually translated as "soul" or "spirit" The ka came into existence when an individual was born.
The ka is usually translated as "soul" or "spirit" The ka came into existence when an individual was born. - Maat

Represents truth, justice, morality and balance. Deities are often seen standing on this symbol, as if standing on a foundation of Maat.
Neter
- The Gods or having to do with the gods.
Palm Branch
- The Egyptians would put a notch in a palm branch to mark the passing of a year in the life of a pharaoh. It symbolized the measure of time.
Pet

This symbol depicts the sky as a ceiling which drops at the ends, the same way the real sky seems to reach for the horizon. It symbolizes the heavens.
Primordial mound
The Egyptians believed that during creation this hill rose out of the sea of chaos to create dry land.
Ra
 The sun was the primary element of life in ancient Egypt, we find this importance reflected in the art and religion. Some of the most popular gods had a solar connection.
The sun was the primary element of life in ancient Egypt, we find this importance reflected in the art and religion. Some of the most popular gods had a solar connection. Sa
Scarab
This is a representation of the pavilion used in the Heb-Sed ceremonies.
Sekhem
Sesen
 A Lotus Flower. This is a symbol of the sun, of creation and rebirth. Because at night the flower closes and sinks underwater, at dawn it rises and opens again. According to one creation myth it was a giant lotus which first rose out of the watery chaos at the beginning of time.
A Lotus Flower. This is a symbol of the sun, of creation and rebirth. Because at night the flower closes and sinks underwater, at dawn it rises and opens again. According to one creation myth it was a giant lotus which first rose out of the watery chaos at the beginning of time.She
 A pool of water. The Egyptians portrayed bodies of water by means of equally spaced vertical wave lines. When these lines are inclosed by a rectangle it denotes a lake or pool. The Egyptians believed water was the primeval matter from which aII creation began.
A pool of water. The Egyptians portrayed bodies of water by means of equally spaced vertical wave lines. When these lines are inclosed by a rectangle it denotes a lake or pool. The Egyptians believed water was the primeval matter from which aII creation began. Shen
Shenu
Sistrum
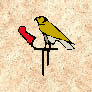
Rekhyt
 This bird is called the Lapwing, it is identified by its head crest, Its wings are pined back preventing it from flying. This symbol signifies a group of people.
This bird is called the Lapwing, it is identified by its head crest, Its wings are pined back preventing it from flying. This symbol signifies a group of people. Tiet
Udjat
Uraeus
Ushabtis
Was
Winged Solar Disk